China and the United States have jointly committed to reduce CO2 emissions "by around 2030". Under the terms of the agreement, the United States will seek to reduce its CO2 emissions by 26%-28% by 2025 compared to 2005 levels, with an effort to reach a 28% reduction. This would reduce US emissions to about 4.1 MtCO2 (from 5.8 MtCO2 in 2005). China intends to achieve a peaking of CO2 emissions around 2030 and to raise the share of non-fossil fuels in primary energy consumption to about 20% by 2030 (less than 10% in 2013).
The two countries have also established the US-China Climate Change Working Group (CCWG), to jointly launch initiatives on vehicles, smart grids, carbon capture, utilization and storage, energy efficiency, greenhouse gas data management, forests and industrial boilers. They will work together to phase down hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs); in June 2013, USA and China had announced that they would work with other countries to reduce HFCs potentially by as much as 90 GtCO2 by 2050.
CO2 emissions from fuel combustion have dropped by 8% and have soared by 60% since 2005 in the USA and in China respectively.
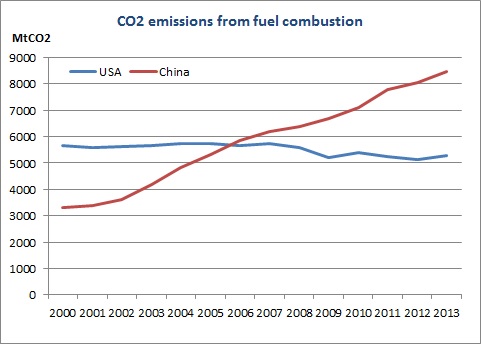
Source: Enerdata

Interested in Global Energy Research?
Enerdata's premium online information service provides up-to-date market reports on 110+ countries. The reports include valuable market data and analysis as well as a daily newsfeed, curated by our energy analysts, on the oil, gas, coal and power markets.
This user-friendly tool gives you the essentials about the domestic markets of your concern, including market structure, organisation, actors, projects and business perspectives.
 Energy and Climate Databases
Energy and Climate Databases Market Analysis
Market Analysis