The China’s national Energy Research Institute, the China State Grid Energy Research Institute and partners released a study envisioning that renewable energy sources (RES) could represent 53% of China power mix in 2030 and 86% in 2050, under the high RES penetration scenario. Wind and solar would be the two major pillars of the RES power production surge, contributing to drastically reduce the coal consumption from 3,500 TWh in 2011 to 1,000 TWh in 2050. Meanwhile, wind energy generation would rise from 97 TWh in 2011 to 5,350 TWh in 2050 and solar from 5 TWh in 2011 to 4,310 TWh to 2050. As a consequence, the CO2 emissions would drop by 60% over the period. In 2050, the contribution of total added value of related renewable energy industries to GDP in 2050 is estimated to increase from a mere 0.9% in 2010 to 6.2% in 2050. The study supposes China’s GDP would increase grows sevenfold between 2010 and 2050, while its population will keep stable at around 1.3-1.4 billion inhabitants. No detail data have been released about the reference scenario.
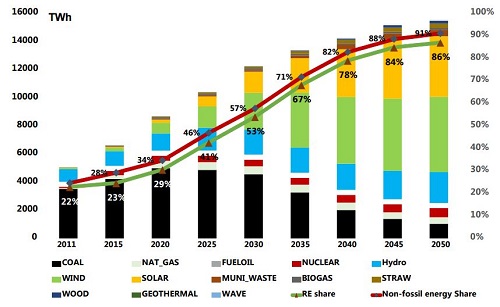
Source: China Energy Research Institute

Interested in Global Energy Research?
Enerdata's premium online information service provides up-to-date market reports on 110+ countries. The reports include valuable market data and analysis as well as a daily newsfeed, curated by our energy analysts, on the oil, gas, coal and power markets.
This user-friendly tool gives you the essentials about the domestic markets of your concern, including market structure, organisation, actors, projects and business perspectives.
 Energy and Climate Databases
Energy and Climate Databases Market Analysis
Market Analysis